Gastric cancer staging ajcc eighth edition duncan mcleod westmead hospital, nsw. Stomach Cancer Staging Radiology summary of changes •new clinical stage prognostic groups, ctnm •postneoadjuvant therapy pathologic stage groupings, yptnm new prognostic information •change to anat. See full list on radiopaedia. org. Search for results at etour. com. check out results for your search.
If you have been diagnosed with adenocarcinoma cancer, you have a cancer that developed in one of the glands that lines the inside of your organs. adenocarcinoma cancers being usually in one of the following organs: prostate, breast, colon,. Signs and symptoms of stomach cancer€ early-stage stomach cancer (gastric cancer) rarely causes symptoms. in countries where screening for stomach cancer is not routine, such as the united states, most stomach cancers aren’t found until they’ve grown fairly large or have spread outside the stomach. A diagnosis of lung cancer naturally causes some overwhelming emotions, but you don’t have to let those emotions get the best of you. information is a powerful weapon against uncertainty and fear, and you can use this to your advantage. whe. The staging system most often used for stomach cancer is the american joint committee on cancer (ajcc) tnm system, which was last updated in 2018.
What Are The Stages Of Lung Cancer
In the past, ct has been the imaging modality of choice Stomach Cancer Staging Radiology for the preoperative staging of gastric cancer and the follow-up of affected patients. however, fdg pet may be superior to anatomic imaging modalities in the detection of distant metastases and significant nodal metastases. in addition, fdg pet may play a valuable role in monitoring response to therapy in patients who undergo surgery or. Ct is currently the staging modality of choice because it can help identify the primary tumor, assess for the local spread, and detect nodal involvement and distant metastases 1. demonstration of lesions facilitated by negative contrast agents (water or gas): a polypoid mass with or without ulceration. Jan 22, 2021 · the staging system most often used for stomach cancer is the american joint committee on cancer (ajcc) tnm system, which was last updated in 2018.
Helical ct evaluation of the preoperative staging of gastric.
Accurate preoperative staging of gastric cancer and the assessment of tumor response to neoadjuvant treatment is of importance for treatment and prognosis. current imaging techniques, mainly endoscopic ultrasonography (eus), computed tomography (ct) and 18f-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (18f-fdg pet), have their limitations. It is an aggressive tumor with a 5-year survival rate of less than 20%. prognosis is correlated to the stage of the tumor at presentation. therefore, accurate staging of gastric cancer is essential because surgical resection is the treatment for localized disease 1. 1. Stomach Cancer Staging Radiology perforation with peritonitis: rare (thought to occur in ~2% of cases) 5,6. Computed tomography (ct) has remained the modality of choice for the preoperative staging of gastric cancer and for follow-up. a recently developed advanced ct technique that makes use of thin sections, optimal contrast material enhancement, and multiplanar reformation allows more accurate staging.
Gastric adenocarcinoma, commonly, although erroneously, referred to as gastric cancer, refers to a primary malignancy arising from the gastric epithelium. it is the most common gastric malignancy. it is the third most common gi malignancy following colon and pancreatic carcinoma. Breast cancer is the second most common cancer found in women — after skin cancer — but that doesn’t mean men aren’t at risk as well. although the percentage of cases in men is much lower than in women, male breast cancer accounts for a por. Gastric cancer is rare before the age of 40, but its incidence steadily climbs after that and peaks in the seventh decade of life 2. the median age at diagnosis of gastric cancer in the united states is 70 years for males and 74 years for females.
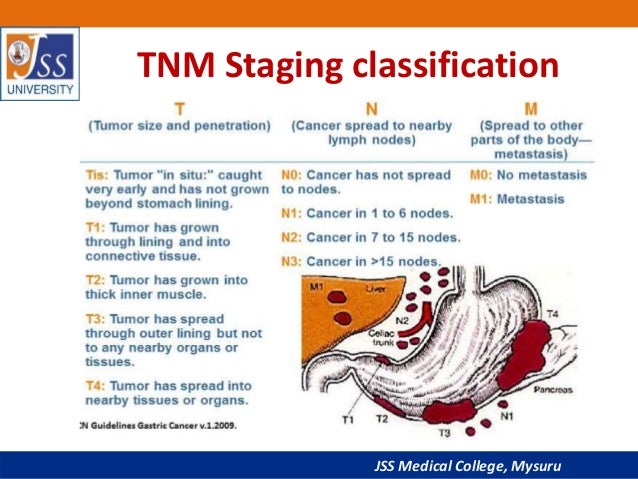
Gastric cancer staging is routinely performed using the tnm staging system. this article is based on the 7th edition of the Stomach Cancer Staging Radiology tnm classification of malignant tumors. tnm staging (7 th edition). The tnm system is the most widely used cancer staging system. most hospitals and medical centers use the tnm system as their main method for cancer reporting. you are likely to see your cancer described by this staging system in your pathology report, unless you have a cancer for which a different staging system is used. examples of cancers. It often produces no specific symptoms when it is superficial and potentially surgically curable, although up to 50% of patients may have nonspecific gastrointestinal complaints such as dyspepsia 2. patients may present with anorexia and weight loss (95%) as well as abdominal pain that is vague and insidious in nature. nausea, vomiting, and early satiety may occur with bulky tumors that obstruct the gastrointestinal lumen or infiltrative lesions that impair stomach distension 2. several nodal metastases with eponymous names associated with gastric cancer have been described: 1. sister mary joseph’s node 2. virchow’s node 3. krukenberg’s node 4. irish node. Check out results on internetcorkboard. com. find info here.
Search And Find Now
Endoscopy is regarded as the most sensitive and specific diagnostic method in patients suspected of harboring gastric cancer. endoscopy allows direct visualization of tumor location, the extent of mucosal involvement, and biopsy (or cytologic brushings) for tissue diagnosis 3. but radiological methods are often the initial examination that Stomach Cancer Staging Radiology raises suspicion for gastric carcinoma, besides being used in the staging of the disease. early gastric cancer (elevated, superficial, shallow): 1. type i:elevated lesion, protrudes >5 mm into the lumen (polypoid) 2. type ii:superficial lesion (plaque-like, mucosal nodularity, ulceration) 3. type iii: shallow, irregular ulcer crater with adjacent nodular mucosa and clubbing/fusion/amputation of radiation folds 4 advanced gastric cancer: 1. polypoid cancer can be lobulated or fungating 2. lesion on a dependent or posterior wall; filling defect in barium pool 3. lesion on non-dependent or anterior wall; etched in white by a thin layer of barium trap On this page: you will learn about how doctors describe a cancer’s growth or spread. this is called the stage. use the menu to see other pages. staging is a way of describing where the cancer is located, if or where it has spread, and whethe. Hearing a diagnosis of prostate cancer is life-altering for men. being armed with information is vital to begin the fight.
Ajcc cancer staging manual (8th edition) m amin and s edge. springer, 2017. gastric cancer: esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up e smyth and others, annals of oncology, 2016. volume 27, pages v38–v49. guidelines for the management of oesophageal and gastric cancer.
Check out staging stomach cancer on teoma. find staging stomach cancer here. Whether colon cancer runs in your family or you’re interested in learning about health conditions as part of an effort to improve your well-being, it’s important to understand this type of cancer. according to the american cancer society, a.
0 comments:
Post a Comment